
The HAZMAT Technician annual refresher course is part of the recertification requirements for HAZMAT Technicians. HAZMAT Technicians utilize specialized chemical protective clothing and control equipment and must participate in annual training to maintain their certificate.

HAZMAT Technicians are tasked with stopping the release or potential release of hazardous materials through plugging, patching, or other means necessary. These professionals respond more aggressively to leaks and spills of hazardous materials than even first responders.
The HAZMAT Technician annual refresher course is designed to help technicians complete their HAZMAT certification online on their own terms.
There are many reasons to choose National Environmental Trainers for your HAZMAT training. The HAZWOPER On Mobile allows you to take the course on any device, and you may start and stop as needed while your progress is saved in our system so you can pick up right where you left off.
Download your e-certificate immediately upon completion of the course.
Support is available throughout the course, which features self-grading quizzes and a final exam.
The HAZMAT Technician Refresher course counts as continuing education units (CEUs). This course is accepted for 1.34 Industrial Hygiene CM Points by the American Board of Industrial Hygiene (ABIH) and .8 Continuance of Certification (COC) points from the Board of Certified Safety Professionals (BCSP).
A study timer shows you how much course time you have accrued so you can track your progress.
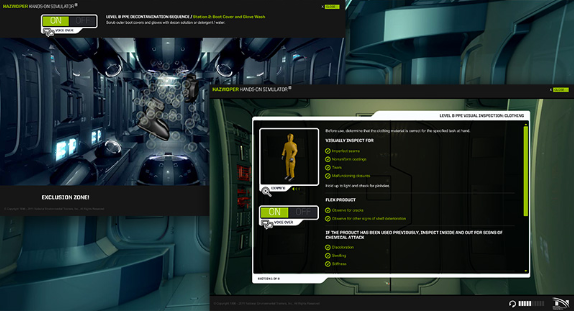
This course includes the OSHA-accepted HAZWOPER Hands-On Simulator®
Learn more about the hands on simulator“Wonderful course and user experience with the HAZMAT Technician Refresher.” – Chase Williams, Babcock & Wilcox
The HAZMAT Technician refresher course consists of 14 videos and over 60 interactive modules of award-winning content. Plus, you'll utilize the HAZWOPER Hands-on Simulator®, the only OSHA-accepted HAZWOPER training component.
The HAZMAT Technician refresher course has been awarded 1.34 Industrial Hygiene CM Points by the American Board of Industrial Hygiene (ABIH) — approval number 13334. This course is eligible for .80 Continuance of Certification (COC) points from the Board of Certified Safety Professionals (BCSP).
The HAZMAT Technicians annual refresher course is required training for individuals planning to work as an emergency first responder. The course follows a modular format which allows employers to select the skills most needed for their hazardous materials team. The training includes offensive procedures for the mitigation of spills, leaks, and exposures to hazardous materials and topics include:
Students are allowed to complete the course at their own pace, as OSHA requires a list of completed competencies rather than a minimum time requirement. Students will earn a certificate of completion accepted by regulatory agencies upon completion of the course. Upon successful completion of the course, students will have learned how to:
The 24-hour HAZMAT Technician course is required as a prerequisite to the HAZMAT Technician annual refresher.
Our training is taken online. As with any training (classroom or online) the employer is required by regulations to train the employee(s) on performance-based standards for any applicable equipment. This is a site-specific requirement and typically cannot be achieved in a regular public seminar or open enrollment class where training on a respirator(s) or PPE in general does not meet the site-specific regulatory requirement. Generic hands-on training on PPE and equipment does not fully meet the OSHA regulations.
Plan States (approved by U.S. OSHA) must have standards at least as stringent as the Federal HAZWOPER training requirements. These Plan States may have additional training requirements.